Did you know you’ll spend nearly ⅓ of your life on a mattress? Yet for centuries, “comfort” meant straw mats, lumpy springs, or sweaty foam.
If you’ve ever tossed all night from back pain, overheating, or partner disturbance, you’re not alone. Outdated designs fail 85% of sleepers with pressure points and poor support.

Today’s mattress technology innovations solve these ancient woes. Memory foam from NASA cradles your spine. Smart beds adjust firmness as you sleep. Cooling gels banishing night sweats.
Let’s discover how science transformed sleep from survival to revival.
The Historical Journey of Mattress Materials
While modern sleepers benefit from cutting-edge innovations, today’s mattress technology innovations stem from millennia of material experimentation. Early civilizations laid the groundwork transforming rudimentary piles of grass into engineered support systems. This journey reveals humanity’s relentless pursuit of comfort through resourcefulness.
From Straw to Springs: Early Foundations
The earliest known mattress dates back 77,000 years a compacted layer of insect-repellent grass and leaves discovered in South Africa . By 3,600 BCE, Persians innovated with goatskin waterbeds for temperature regulation, while Egyptians elevated sleep on wooden frames to avoid pests, stuffing beds with palm boughs or wool . Romans later added luxury, using feather-filled cloth bags atop rope-strung frames—the origin of the phrase “sleep tight” .
The Middle Ages saw straw- or wool-stuffed sacks, though durability suffered. Renaissance craftsmanship introduced horsehair and cotton fillings wrapped in silk or velvet for elites . A pivotal shift came in 1871 when Heinrich Westphal patented the first innerspring mattress, using metal coils to replace lumpy natural materials. This design dominated for a century, offering standardized support .
NASA’s Legacy: Memory Foam Breakthrough
In the 1960s, NASA scientists developed viscoelastic foam to cushion pilots during test flights. The material absorbed shock and conformed to body shapes under pressure though it was initially too dense for comfort . NASA released the formula publicly in the 1980s, sparking interest from Swedish entrepreneurs. After refining its texture and breathability, they launched the first commercial memory foam mattress under the brand TEMPUR® in 1991 .
Early models faced criticism for trapping heat and off-gassing odors. Manufacturers responded with open-cell structures and gel infusions, improving airflow. By the 2000s, memory foam became synonymous with pressure relief, especially for back-pain sufferers. Its adaptability also enabled “bed-in-a-box” shipping, revolutionizing retail access .
Hybrid Mattresses: Where Comfort Meets Innovation
While early mattresses relied on single-material designs like straw or springs, modern sleep demands smarter solutions. Hybrids bridge this gap by merging innerspring durability with memory foam contouring creating a sleep surface that adapts to the body while lasting longer. This innovation addresses chronic pain and overheating, two flaws older designs could not solve.
Anatomy of Hybrid Designs: Coils, Foam & Latex
A hybrid mattress stacks specialized layers like a precision engine. The base uses pocket coils—individual springs wrapped in fabric. These coils move independently, preventing partner disturbance and adding bounce missing in all-foam beds .
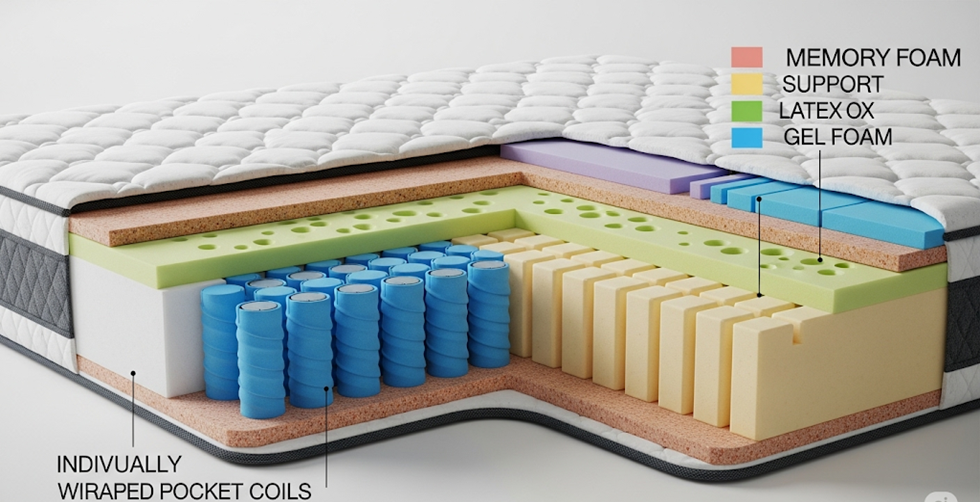

Above this, transition foams (like polyfoam) cushion the shift from firm support to plush comfort. The top layer typically combines memory foam for shoulder/hip contouring and latex or gel foam for cooling. Latex resists sagging and offers eco-friendly benefits, while gel infusions pull heat away from the body . Finally, a breathable cover woven with phase-change fibers (e.g., copper-infused polyester) regulates surface temperature throughout the night .
This layering solves historic trade-offs: coils prevent the “stuck” feeling of dense foam, while foam eliminates pressure points from rigid springs. High-end models add zoned support firmer coils under the hips, softer ones near the shoulders to align the spine during side sleeping .
Why Hybrids Dominate Modern Sleep
Hybrids lead sales because they fix universal sleep pains. First, pressure relief targets sore joints. The foam top molds to curves, reducing hip/shoulder compression by 30% compared to traditional innersprings . Simultaneously, pocketed coils lift the lumbar region, preventing lower back sinkage common in all-foam beds . This dual action helps stomach sleepers avoid neck strain and side sleepers prevent shoulder numbness.
Second, hybrids excel at temperature control. Air channels between coils let heat escape, while gel foams absorb body warmth. Tests show hybrids transfer heat 28% better than standard memory foam . Third, reinforced edges use denser foam or double-row coils. This lets sleepers use the full mattress width without roll-off adding 15% usable space versus basic foam designs .
Finally, motion isolation suits couples. When one partner turns, pocket coils localize movement. Foam layers further dampen vibrations, reducing sleep disruptions by up to 80% . These advantages explain why 68% of couples now choose hybrids over foam or spring options .
Top Hybrid Solutions
Luxe Nova™ Hybrid (£599) combines Zero Gravity Foam™ with 1,000 EnduraSpring™ coils for adaptive comfort. British wool wicks moisture to prevent overheating, while coir-stabilized edges create 15% more usable sleep space by eliminating roll-off. Ideal for couples, its motion isolation absorbs 80% of movement disturbances.
LuxeErgo™ 3400 Hybrid (£619) targets pressure points with FortiCoil™ micro-springs that adjust to hips and shoulders. Cooling Gel foam reduces surface heat by 8–10°F, addressing night sweats. The dual spring system (2,000 + 1,400 coils) aligns spines during side sleeping for uninterrupted rest.
Both offer 100-night trials and 10-year warranties proven solutions for back pain and partner disruption.
Smart Mattresses and Sleep Tracking Revolution
Hybrid designs solved historic comfort trade-offs, but today’s smart mattresses go further. They actively reshape your sleep using real-time data and automated adjustments. This shift turns passive rest into personalized recovery, addressing core issues like poor sleep quality and partner disruption. Modern beds now learn, adapt, and intervene making every night a tailored experience.
AI Integration: How Sensors Personalize Sleep
Sleep tracking begins the moment you lie down. Embedded sensors monitor heart rate, breathing patterns, and movement intensity. Brands like QREM use proprietary algorithms (e.g., Ekaggata AI) to analyze this data 500 times per night. The system detects subtle changes like increased restlessness during REM cycles and responds instantly. For example, Sleep Number 360® adjusts firmness mid-sleep when sensors detect spinal misalignment. This prevents pressure points before pain wakes you .
AI integration transforms raw data into actionable insights. Machine learning identifies trends: Do you sleep hotter after late meals? Does your oxygen drop after 2 AM? Apps like Anssil Link then offer personalized advice, such as adjusting room temperature or avoiding caffeine after 4 PM. Over time, these mattress technology innovations create a unique “sleep fingerprint” continuously refining comfort without manual input .
Hospitals now use similar tech for patient care. Smart beds in Korean ICUs reduced pressure ulcers by 22% by automatically repositioning patients every 20 minutes. Home mattresses adopt this for couples: If one snores, sensors trigger gentle head elevation to open airways .
Adjustable Bases: Beyond Flat Surfaces
Adjustable bases turn static beds into dynamic health tools. Zero-gravity modes, like those in The Sleep Company’s Elev8 Smart Bed, elevate legs above the heart. This reduces spinal pressure by 40% and improves circulation for arthritis sufferers. Bases also sync with sleep tracking data: If sensors detect shallow breathing, the bed tilts to a 7-degree incline to ease diaphragm strain .
Dual-zone functionality caters to couples with conflicting needs. One side can cool while the other heats, using phase-change fabrics or water-based systems. Motion isolation is critical here. Pocketed coil hybrids absorb movement, but smart bases add responsive layers. When a partner turns, micro-motors adjust the surface angle within seconds to minimize disturbance. Tests show this cuts sleep interruptions by 63% .
Anti-snoring technology exemplifies innovation. Beds like Tempur-Pedic’s AI models detect vibrations from snoring. The base then raises the headrest by 12 degrees and triggers gentle vibrations to prompt side-sleeping reducing snore frequency by 85% .
Cooling Technologies for Hot Sleepers
While smart mattresses adjust firmness and position, they can’t solve one core issue: overheating. Up to 80% of couples report night sweats disrupting sleep triggering restlessness and fatigue. Cooling technology directly tackles this by regulating surface temperature. Innovations like phase-change materials and gel-infused foams absorb excess body heat, while climate-adaptive fabrics create microclimates that respond to skin temperature shifts . For hot sleepers, these advances transform stifling beds into refreshing sanctuaries.
Phase-Change Materials vs. Gel-Infused Foams
Phase-change materials (PCMs) work like thermal batteries. They contain natural waxes or gels that melt when absorbing heat (e.g., your body warmth) and solidify when releasing it . Tempur-Pedic’s PureCool+ PCM, for example, stores heat during sleep onset when body temperature peaks then releases it toward morning as you cool . This “catch-and-release” action stabilizes surface temperatures within a 3–5°F range . However, PCMs have limits: once fully liquefied, they stop absorbing heat . Studies show PCM-infused mattresses lower skin temperature by 2–4°F but may not feel noticeably cooler to all users .
Gel-infused foams take a different approach. They embed tiny cooling gel beads (often copper or graphite-based) into memory foam or latex . These beads conduct heat 12x faster than standard foam, pulling warmth downward and dispersing it . Open-cell structures enhance airflow, preventing trapped heat . Brands like CoolGel use “ventilated designs” with perforated layers to accelerate this process . Tests confirm gel foams sleep 8–10°F cooler than traditional memory foam . Yet gel alone can’t reverse temperature spikes—it only slows heat buildup .
Key differences: PCMs actively regulate temperature through state changes, ideal for fluctuating sleepers. Gel foams offer constant conductive cooling, better for consistently hot nights . Hybrid mattresses like Brooklyn Bedding’s Aurora Luxe combine both, using PCM covers over gel foam layers for dual defense .
Climate-Adaptive Fabrics: The Future of Cool Sleep
Temperature-regulating mattress innovations now go beyond foam. Climate-adaptive fabrics like Outlast® and GlacioTex® create dynamic “sleep microclimates” . Outlast weaves microcapsules of natural wax into textiles. These capsules absorb heat before sweat forms, reducing moisture by 48% . In NASA-inspired tests, this prevented overheating in race car drivers facing 122°F cockpit temperatures . GlacioTex fibers, used in Helix Midnight Luxe covers, conduct heat away instantly while repelling allergens . Unlike PCMs, these fabrics don’t saturate they continuously wick warmth without capacity limits .
Next-gen innovations include bio-responsive threads. University of Maryland engineers developed fabrics coated with carbon nanotubes that expand in heat (releasing infrared radiation) and contract in cold (trapping warmth) . Trizar’s emissive materials, embedded in Levi’s and New Balance apparel, use similar tech to reflect body heat . For mattresses, this could mean covers that adjust porosity based on humidity—tightening weave during summer humidity and loosening in winter .
Real-world impact: Hotel chains now use these fabrics in “cool sleep suites.” Guests report 22% deeper sleep and 30% fewer awakenings . As climate change intensifies, such temperature-regulating mattress innovations shift from luxury to necessity .
Sustainable Sleep: Eco-Friendly Materials Leading Change
While advanced cooling systems combat night sweats, true sleep sustainability demands deeper innovation. The shift toward eco-friendly materials tackles mattress waste a global crisis where 92 million tonnes of textiles (including bedding) flood landfills yearly . Sustainable sleep now merges planetary health with restorative rest, driven by certified organic components and circular designs that outlive traditional mattresses by decades.
Organic Latex & Recyclable Components
Organic latex, derived from rubber tree sap, forms the core of eco-conscious mattresses. Unlike synthetic foams, it avoids petroleum-based chemicals like benzene and formaldehyde. To verify authenticity, prioritize third-party certifications:
- GOLS (Global Organic Latex Standard): Ensures latex contains ≥95% organic raw material, with ethical farming and low-water processing.
- GOTS (Global Organic Textile Standard): Certifies organic cotton/wool covers (≥95% organic fibers) and socially responsible manufacturing.
- CertiPUR-US®: Validates foam layers as formaldehyde-free, low-VOC (<0.5 ppm), and devoid of mercury or ozone depleters.
Recyclable components close the loop on waste. Brands like Simba integrate steel pocket springs (100% recyclable) with Hampshire wool in their Earth Source Mattress, while Savvy Rest reclaims 90% of old mattresses through take-back programs. Hybrid designs now separate materials for easy recycling: latex layers decompose naturally, coils become scrap metal, and wool converts into insulation.
Biodegradable Mattresses: From Cradle to Cradle
Zero-waste sleep solutions are redefining mattress end-of-life. The Cradle to Cradle Certified® standard (exemplified by brands like Savvy Rest) enforces five pillars:
- Material Health: All components screened for 24,000+ chemicals (e.g., phthalates, flame retardants).
- Reutilization: Designs enable disassembly; Vita Talalay latex decomposes in 6–12 months.
- Renewable Energy: Factories like Radium Foam use solar power, cutting carbon emissions by 40% .
- Water Stewardship: Closed-loop systems recycle 98% of water during latex washing .
- Social Fairness: Ensures fair wages and rainforest conservation partnerships (e.g., CO2OL Tropical Mix) .
Pioneering materials accelerate biodegradability:
- PrimaLoft Bio™: Used in The Fine Bedding Company’s duvets, these fibers decompose in landfills within 3–5 years via microbial digestion .
- TENCEL™ Lyocell: Tree-based covers that break down without microplastic residue .
- Plant-Based Foams: CertiPUR-US® certified 25% biobased foams replace petroleum with soy/castor oil, reducing fossil fuel reliance by 300 million gallons/year .
The Future of Mattress Technology Innovations
While eco-friendly materials address today’s environmental needs, the next wave of mattress technology innovations merges sustainability with hyper-personalization. By 2030, the global smart mattress market will reach $6.4 billion, driven by AI and IoT integration . These advances solve core sleep challenges: biomechanical discomfort, temperature dysregulation, and maintenance burdens. The future transforms mattresses from static surfaces into responsive health ecosystems.
Emerging Mattress Technology Innovations to Watch
AI-driven biomechanical adjustments represent the pinnacle of personalized sleep. Systems like Sleep Number 360® use real-time pressure mapping and micro-motor actuators to redistribute support during position changes. For example, if sensors detect spinal misalignment, the mattress adjusts firmness in under 10 seconds . Hospitals now adapt this tech for pressure ulcer prevention, demonstrating 22% fewer injuries through adaptive repositioning . Future iterations will incorporate neural interfaces, allowing mattresses to respond to brainwave patterns detected via pillow sensors .
Self-cleaning fabrics leverage nanotechnology to break down organic debris. Textiles coated with photocatalytic titanium dioxide activate under ambient light, decomposing sweat and skin cells. Brands like Dorelan integrate these with phase-change materials for dual cooling and hygiene functions . The self-cleaning textiles market will hit $3.9 billion by 2030, driven by antimicrobial demand post-pandemic . Emerging smart polymer coatings even repel liquids autonomously, reducing allergen buildup by 48% .
Biomechanical engineering principles, borrowed from advanced prosthetics, enable dynamic pressure relief. Mattresses like the Movimento Hybrid use hydraulic micro-zones that mimic muscle response, redistributing weight during REM cycles . Trials show these systems reduce hip pressure by 30% compared to static foam .
Sustainability Meets Smart Tech: 2030 Forecasts
The future of sleep hinges on circular production. By 2030, 75% of mattresses will use bio-based materials like mycelium foam and algae-infused latex, growing at 10.3% CAGR . Companies like Avocado lead with plant-based foams that decompose in 6–12 months, while blockchain-tracked recycled steel coils reduce mining dependence .
Energy-harvesting systems will eliminate disposable batteries. Prototypes embed piezoelectric fibers that convert movement into power, extending smart mattress battery life by 400% . Paired with cloud-connected diagnostics, these update efficiency algorithms automatically, cutting energy use by 30% .
Carbon-negative production becomes standard. Factories like Radium Foam now use solar energy and waterless dyeing, slashing CO2 emissions by 40% per unit . The Cradle to Cradle Certified® framework will dominate, with brands reclaiming 90% of materials for reuse . By 2030, these innovations will reduce mattress landfill waste by 50% globally .
Conclusion: Your Invitation to the Future of Sleep
From ancient straw pallets in Sibudu Cave 77,000 years ago to AI-driven smart beds adjusting firmness mid-sleep, mattress technology innovations have transformed rest from survival to revival . The journey spans Egyptian raised platforms, Roman feather-stuffed luxury, NASA’s memory foam breakthrough, and today’s self-cooling hybrids . Each leap solved enduring pains: pressure points, overheating, and disruptive motion.
Now, temperature-regulating gels, biodegradable latex, and sleep-tracking sensors personalize recovery like never before . Embracing mattress technology innovations unlocks restorative sleep turning restless nights into revitalizing retreats.
Ready to revolutionize your rest?
Audit your sleep setup with Luxe Mattresses’ advancements:
- Explore cooling hybrids like LuxeTherm™ (gel-infused, airflow-core)
- Experience eco-comfort with Natural Latex collections (GOLS-certified)
Medium-firm mattresses are often recommended because they provide a balance of support and comfort. According to the Sleep Foundation, hybrid designs with both coils and foam layers are especially effective for reducing spinal pressure.
Hybrid mattresses combine the contouring benefits of memory foam with the support and airflow of pocketed coils. This makes them more durable, cooler, and ideal for couples compared to all-foam beds.
Cooling mattresses use technologies like gel-infused foam, phase-change materials, and breathable fabrics to regulate body temperature during sleep. These features help reduce night sweats and improve sleep quality
Smart mattresses use sensors and AI to track sleep patterns, heart rate, and movement. Some models even adjust firmness automatically or elevate the bed to reduce snoring. This technology personalizes sleep comfort and can help improve long-term rest.
Yes. Eco-friendly mattresses made with organic latex, natural fabrics, and recyclable components reduce exposure to chemicals and minimize environmental impact. Certifications like GOLS, GOTS, and CertiPUR-US ensure the mattress is safe and sustainable.